Geometry Optimization in a Workflow
Integrate geometry optimization into you workflow
What is Geometry Optimization and Why Do It?
Geometry optimization is the process of finding the best atomic positions in a molecule. This helps to relax internal forces and lower the molecule’s potential energy.
Molecular databases often store molecules with roughly generated 3D coordinates. These rough structures are not realistic and need optimization. Without this step, the molecular shape will be incorrect, making it unsuitable for tasks like docking and molecular dynamics (MD) simulation.
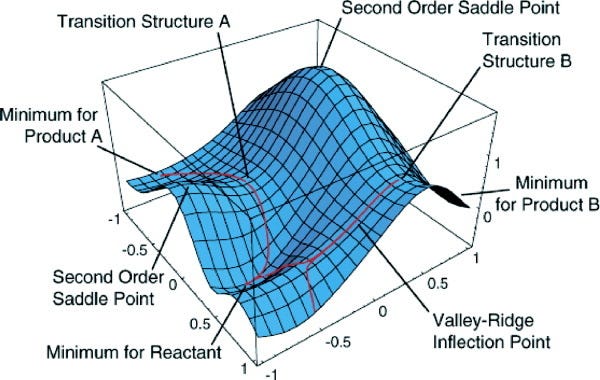
Potential energy surface
A potential energy surface (PES) is a mathematical function that describes how a molecule’s energy changes with different atomic positions. It helps to understand atomic movements and interactions.
There are different ways to calculate PESs:
High-accuracy methods: Post-Hartree-Fock (e.g., CCSD(T), MRCI) give very precise results but are expensive.
Density Functional Theory (DFT): A balance between accuracy and cost, widely used in computational chemistry.
Semi-empirical and Machine Learning methods: Faster and useful for large-scale applications.
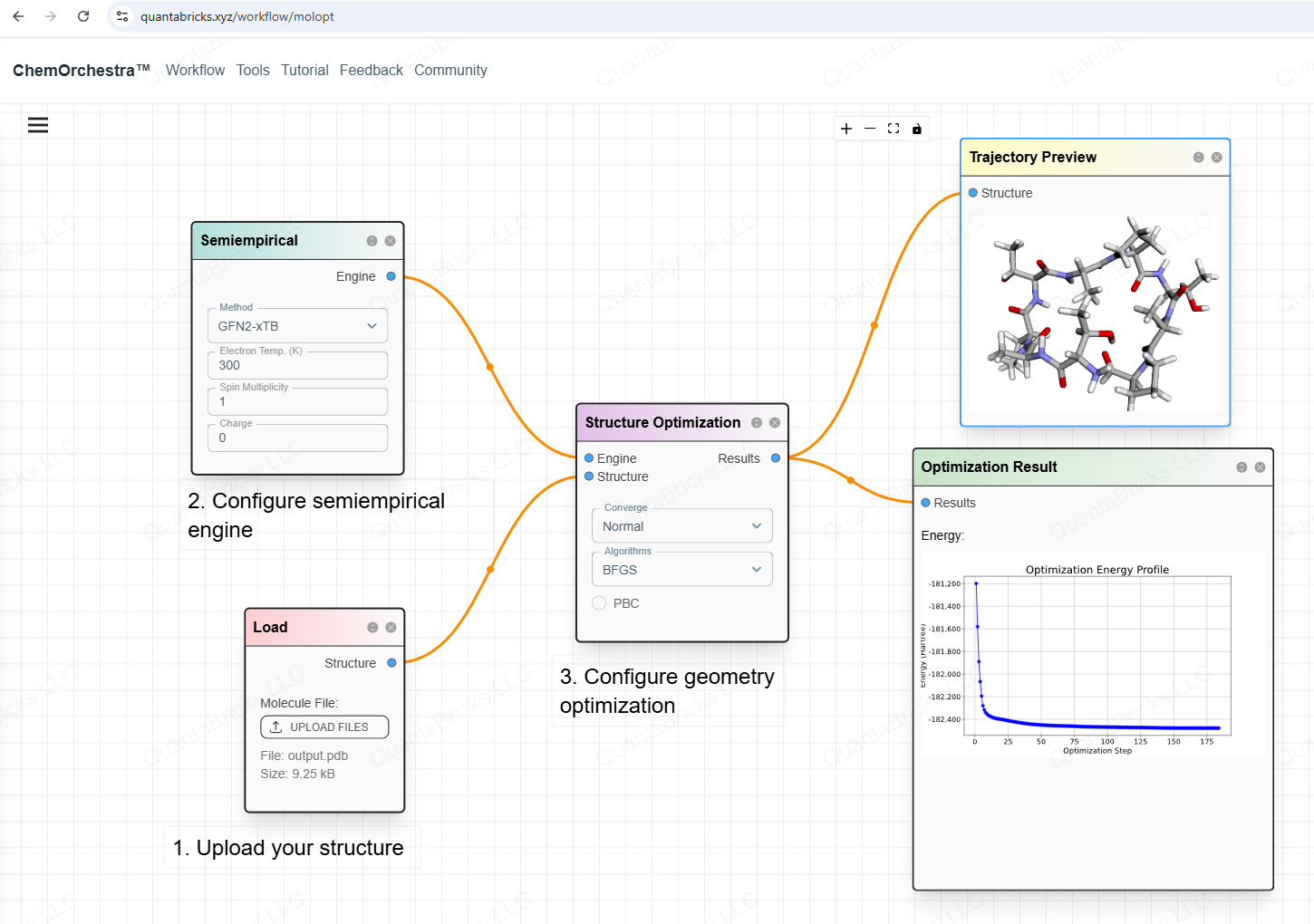
Geometry Optimization on ChemOrchestra
ChemOrchestra makes geometry optimization easy. Users can upload molecular coordinate files in formats like XYZ, PDB, or even SMILES.
The platform allows users to choose different computational engines. For drug-like molecules (mainly C, H, O, N, …), semi-empirical methods like xTB-GFN2 work well.
With ChemOrchestra, users can optimize molecular structures efficiently, making them ready for further simulations and analysis.
Please visit the toolkits of our platform. https://www.quantabricks.xyz/toolkits, you will find more pre-built workflows.
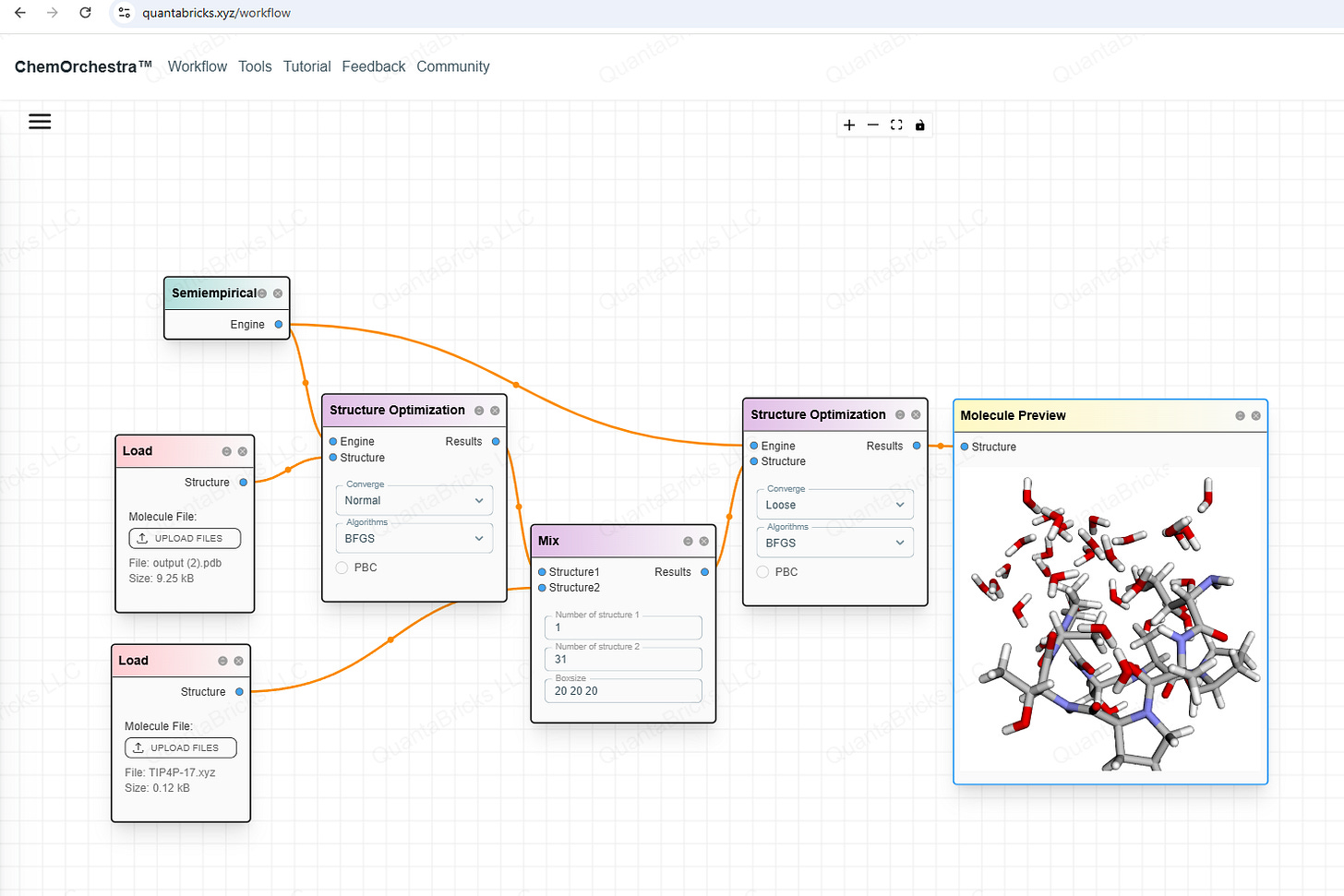
You can even build a more complex workflow, for example, optimizing the solvation structure of a cyclic peptide.